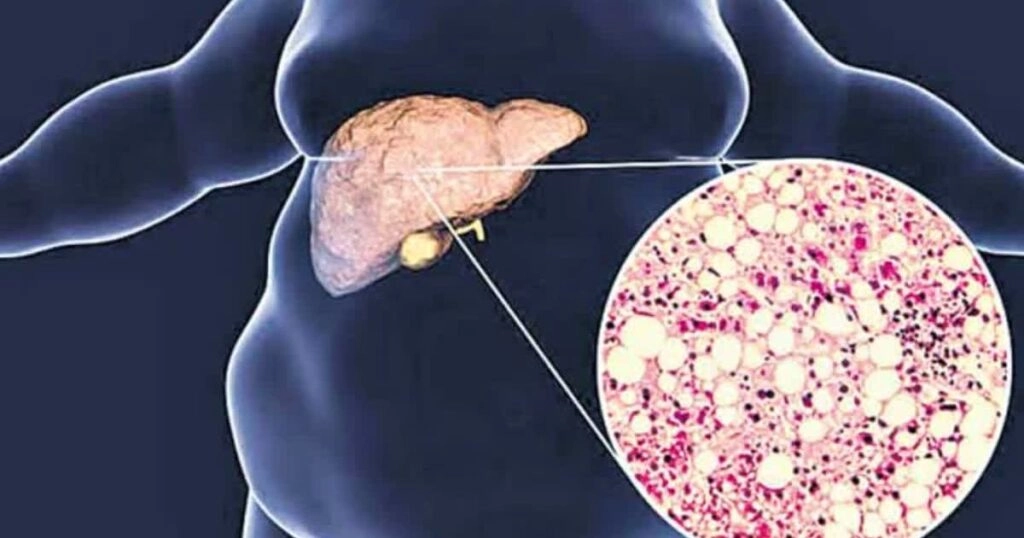
Fatty liver disease, known medically as hepatic steatosis, is a condition characterized by an excessive accumulation of fat in liver cells. Understanding the factors that contribute to this condition can help individuals manage their liver health more effectively. Here are five positive influences that can promote liver health, along with five negative factors that can exacerbate fatty liver disease.
First, maintaining a healthy diet is crucial for combating fatty liver. Consuming foods rich in antioxidants, such as fruits and vegetables, can help reduce liver inflammation and promote fat metabolism. Regular physical activity also plays a significant role; exercise aids in weight management and improves insulin sensitivity, which can help decrease fat buildup in the liver. Staying hydrated by drinking plenty of water supports liver function and helps flush out toxins. Additionally, managing stress through techniques like meditation or yoga can positively impact liver health, as chronic stress may contribute to unhealthy eating habits and lifestyle choices. Finally, regular check-ups with a healthcare professional can help monitor liver health and catch any potential issues early.
On the contrary, several negative factors can worsen fatty liver disease. One of the most significant contributors is excessive alcohol consumption, which can lead to alcoholic fatty liver disease. This condition not only increases fat accumulation in liver cells but can also result in inflammation and liver damage over time. Another detrimental factor is obesity; carrying excess weight, especially around the abdomen, is closely linked to fatty liver. A sedentary lifestyle, characterized by little to no physical activity, can exacerbate weight gain and insulin resistance, further increasing the risk of fatty liver. Moreover, a diet high in refined carbohydrates and sugars can lead to fat accumulation in the liver, as these foods can spike insulin levels and promote fat storage. Lastly, certain medications and toxins can negatively affect liver health, leading to complications associated with fatty liver disease.
In conclusion, recognizing both the positive and negative factors related to fatty liver disease is essential for effective management. By adopting a healthy lifestyle that includes a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management, individuals can significantly improve their liver health. Conversely, avoiding excessive alcohol intake, maintaining a healthy weight, and being mindful of dietary choices are equally important in preventing the progression of fatty liver disease. Through awareness and proactive measures, it is possible to foster a healthier liver and overall well-being.